n-Undecane#
References#
Equation of State#
I. S. Aleksandrov, A. A. Gerasimov, and B. A. Grigor'ev. Using Fundamental Equations of State for Calculating the Thermodynamic Properties of Normal Undecane. Thermal Engineering, 58(8):691–698, 2011. doi:10.1134/S0040601511080027.Surface Tension#
A. Mulero and I. Cachadiña. Recommended Correlations for the Surface Tension of Several Fluids Included in the REFPROP Program. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 43:023104–1:8, 2014. doi:10.1063/1.4878755.Aliases#
Undecane, UNDECANE, N-UNDECANE, C11, NC11H24, n-C11H24
Fluid Information#
Parameter, Value |
|
|---|---|
General |
|
Molar mass [kg/mol] |
0.15630826 |
CAS number |
1120-21-4 |
ASHRAE class |
|
Formula |
C11H24 |
Acentric factor |
0.5390371013718567 |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H24/c1-3-5-7-9-11-10-8-6-4-2/h3-11H2,1-2H3 |
InChIKey |
RSJKGSCJYJTIGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
SMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCC |
ChemSpider ID |
13619 |
Limits |
|
Maximum temperature [K] |
700.0 |
Maximum pressure [Pa] |
500000000.0 |
Triple point |
|
Triple point temperature [K] |
247.541 |
Triple point pressure [Pa] |
0.4460558308906604 |
Critical point |
|
Critical point temperature [K] |
638.8000144673849 |
Critical point density [kg/m3] |
236.79409339482066 |
Critical point density [mol/m3] |
1514.917339587944 |
Critical point pressure [Pa] |
1990452.1527680526 |
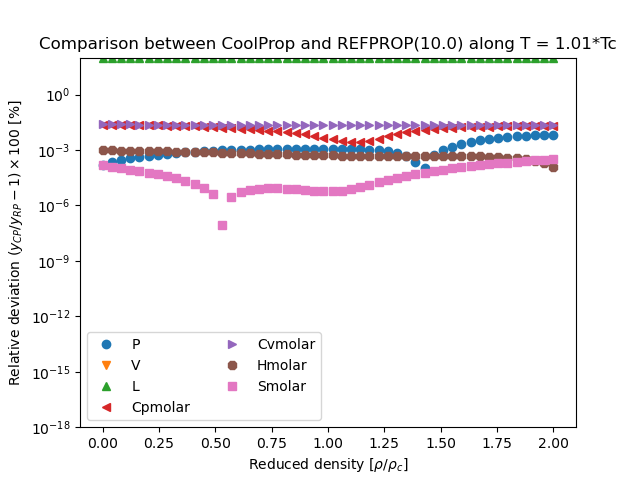
REFPROP Validation Data#
Note
This figure compares the results generated from CoolProp and those generated from REFPROP. They are all results obtained in the form \(Y(T,\rho)\), where \(Y\) is the parameter of interest and which for all EOS is a direct evaluation of the EOS
You can download the script that generated the following figure here: (link to script), right-click the link and then save as… or the equivalent in your browser. You can also download this figure as a PDF.
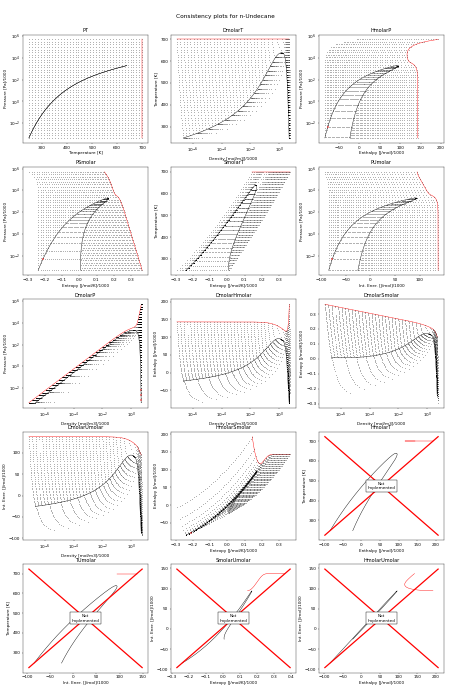
Consistency Plots#
The following figure shows all the flash routines that are available for this fluid. A red + is a failure of the flash routine, a black dot is a success. Hopefully you will only see black dots. The red curve is the maximum temperature curve, and the blue curve is the melting line if one is available for the fluid.
In this figure, we start off with a state point given by T,P and then we calculate each of the other possible output pairs in turn, and then try to re-calculate T,P from the new input pair. If we don’t arrive back at the original T,P values, there is a problem in the flash routine in CoolProp. For more information on how these figures were generated, see CoolProp.Plots.ConsistencyPlots
Note
You can download the script that generated the following figure here: (link to script), right-click the link and then save as… or the equivalent in your browser. You can also download this figure as a PDF.
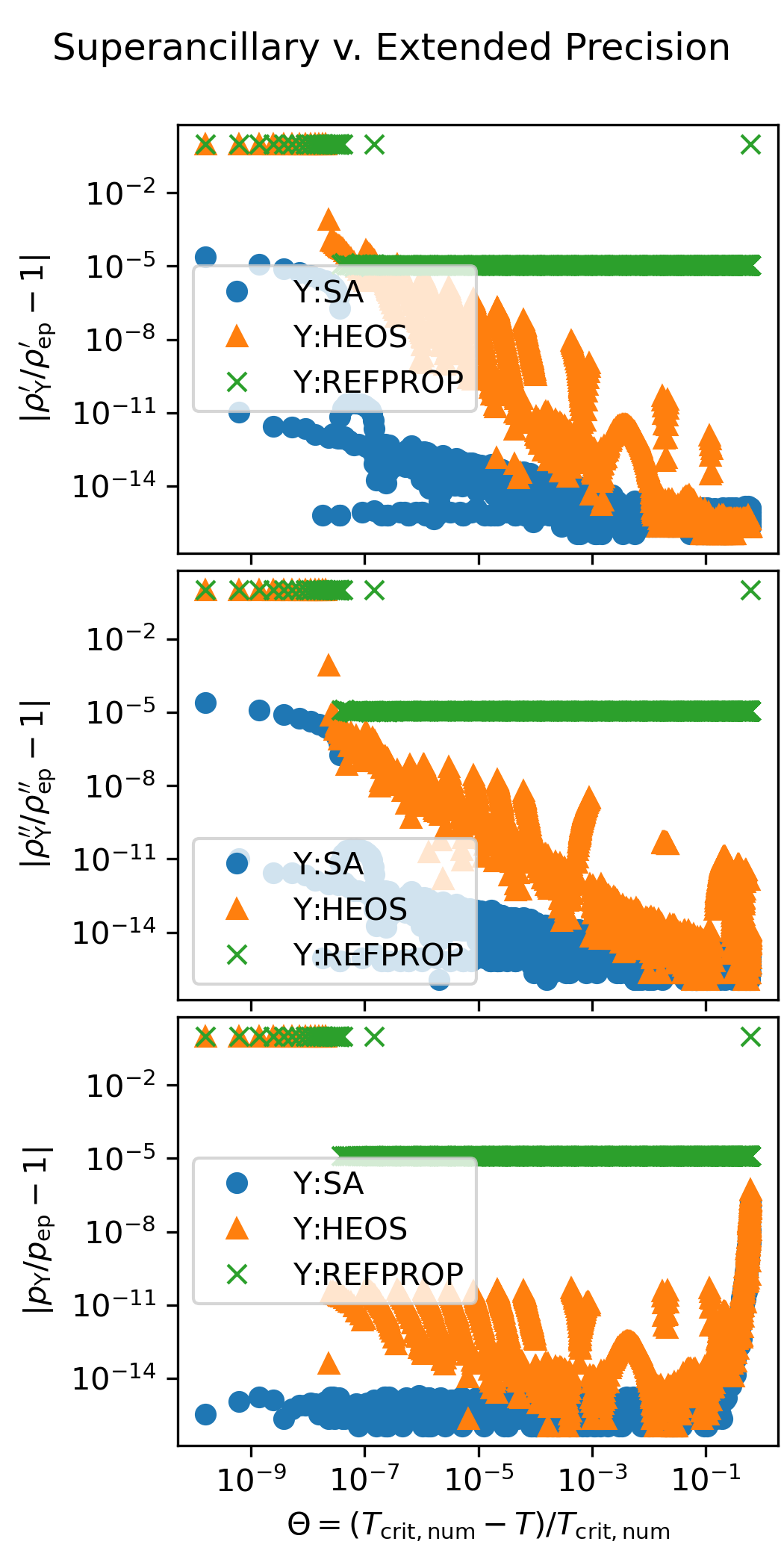
Superancillary Plots#
The following figure shows the accuracy of the superancillary functions relative to extended precision calculations carried out in C++ with the teqp library. The results of the iterative calculations with REFPROP and CoolProp are also shown.
Note
You can download the script that generated the following figure here: (link to script), right-click the link and then save as… or the equivalent in your browser. You can also download this figure as a PDF.